

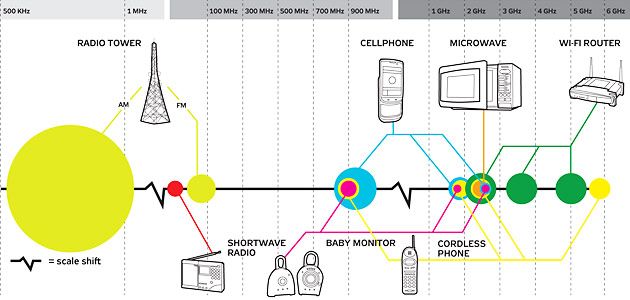
The wavelength of that light is about 12.5 centimeters, which is about 125 million nanometers. In theory, your wireless device should search for and prefer a 5 GHz signal, but will switch to a 2.4 GHz signal if the 5 GHz signal becomes degraded by interference or distance. WiFi operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency range, the same as a microwave oven. If you have a Network Box model GFRG100 or GFRG110, your wireless device searches for and connects to the strongest available signal. The 5 GHz frequency is faster and typically less congested than the 2.4 GHz frequency. If single radio access points are being used, the 2.4 GHz access points can. If you have a Network Box model GFRG200 or GFRG210 and a wireless device that is capable of operating on either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequencies (also called dual-band capable), your Network Box sends a signal to your wireless device to steer, or encourage it to connect to the 5 GHz frequency. FIGURE 2.6 Wavelength formulas Wavelength (inches) 11.811/frequency (GHz). The frequency your wireless devices connect to is based on the capability of your wireless devices, the model of your Network Box, and the physical location of your equipment.
#2.4 ghz wavelength tv#
If you have Fiber TV service, each TV Box has a Wi-Fi radio that supports the following frequencies and protocols: Model GFHD100: The Wi-Fi radio in your Network Box operates on the following frequencies and protocols: Models GFRG100 and GFRG110: You can get the best performance out of your Wi-Fi network by following a few simple optimization guidelines. Protocols are sets of instructions that manage the interaction of the devices and data on your wireless network. Frequency represents the speed at which data is transmitted and received among the devices on your wireless network. You could just use 2.4, but in order to be a little more accurate, we will use two more decimal places. For f, we need to plug in the Wi-Fi frequency. We know v will be 300 (rounded up based on the speed of light mentioned above). Wi-Fi networks operate on two standard frequencies. Wavelength (mm) Velocity of wave (Mm/sec) / Frequency (GHz) w v / f.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
